Table of Contents
While it is more than obvious that both AWS Direct Connect and a regular VPN offer many benefits to their users, one has to be better than the other? Right? Well, not necessarily.
When it comes to these things, it’s not easy saying one’s better than the other, mostly because there are too many factors at play. That’s like saying iPhone’s better than the Android, or the other way around.
In the end, it all boils down to your personal preference and preferred use case scenario.
So, instead of trying to figure out which one’s better – we’ll do you one better. We’ll compare the two, outline their differences, and let you decide which one’s a better fit for your needs.
Sounds good? Let’s go.
What Is AWS Direct Connect?
AWS Direct Connect is a physical connection between your on-premises network and an AWS Direct Connect location.
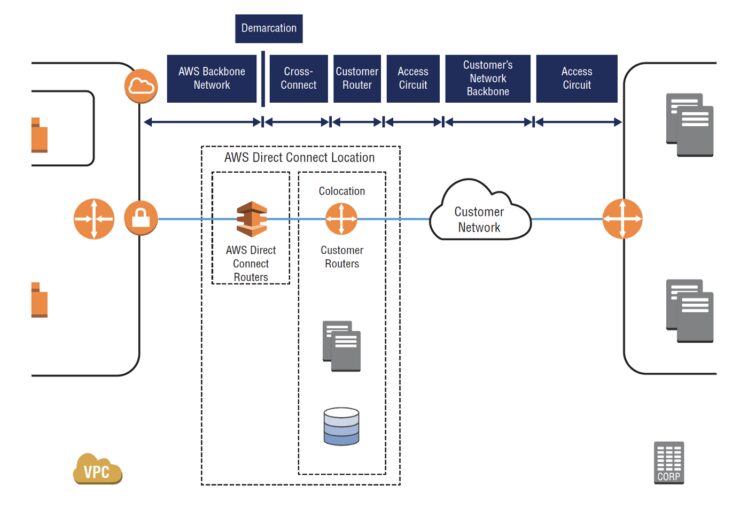
This connection can be used for:
- Improve performance and build hybrid networks by connecting your AWS and on-premises networks to build applications that work in both environments without compromising performance.
- Improved speed in between locations by connecting your network to AWS Direct Connect. You can use SiteLink to send data between your locations. When using SiteLink, the data will travel along the shortest path between locations.
- Manage large databases by making sure your data transfers are quick and easy so you can do real-time analysis, rapid data backup, or broadcast media processing.
What Is VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a private network that extends across a public network, like the Internet. It uses tunnelling protocols to encrypt data at the sending end and decrypt it at the receiving end.

A VPN can be used for:
- Transferring data securely between two or more locations;
- Bypassing geo-restrictions and accessing content that would otherwise be unavailable in your location;
- Protecting your online traffic from snooping, interference, and censorship.
How Do They Differ?
The main difference between AWS Direct Connect and VPN is that Direct Connect provides a physical connection between your on-premises network and an AWS Direct Connect location, while VPN uses a public network to connect two or more locations.
However, the differences don’t end there. Here’s a brief overview of all the differences, but if you’d still like to learn more about the AWS cloud connection – check this out.
- VPN connection requires a single-port connection, whether we’re talking about an AWS-managed VPN or any other run-of-the-mill VPN service. AWS Direct Connect on the other hand requires two.
- To connect to AWS’s service, you’ll need a fibre optic ethernet cable. For a VPN, you just need to download a piece of software and you’ll connect to a private network via an encrypted connection.
- The performance varies greatly. AWSDC speeds can vary from 1 Gbps, all the way up to 100 Gbps, depending on the connection. VPNs can rarely top the 5 Gpbs speeds.
- When it comes to cloud services, a VPN-based cloud can only support up to two tunnels. With AWSDC, the entire region is covered.
- Arguably the biggest difference (for the end user) between the two lies in the cost. Amazon’s service is noticeably more expensive than the regular VPN.
- With Direct Connect, the encrypted connection is created between your router and AWS Direct Connect’s router. With VPN, the connection is established between your network and the VPN service provider.
- AWSDC is far better in terms of security. While undoubtedly safe, VPNs connect to public networks, which leaves room for interference and potential threats. DC’s a closed loop between you and your service provider, in this case, AWS, which means there’s far less chance for any trouble along the way.
- Direct Connect lets you use all the AWS regions. VPN does not let you use all the regions and the performance can be unpredictable. On the same note, VPNs do offer better worldwide coverage.
- AWS Direct Connect is a much better option for enterprise use case scenarios, while VPN’s more geared towards personal use. Also, it’s a lot easier to set up a VPN than it is to set up AWSDC.
Pros & Cons Of Each
To get more familiar with each of these, we’ll take a quick peek at the pros and cons of both.

Let’s start by looking at the pros and cons of Direct Connect.
Pros:
- Faster speeds and more reliable than VPN
- More secure connection
- Can be used with all AWS regions
- Easily scalable
Cons:
- More expensive than a VPN
- Requires a physical connection
- Requires professional set-up
Now, for the VPN.
Pros:
- Extremely affordable
- Straightforward and simple setup
- Worldwide availability
- Excellent for personal use
Cons:
- Often slow and unresponsive
- Not as secure as Direct Connect
- Not as “private” as once thought
Can You Use VPN With AWS Direct Connect?
Yes. In fact, there’s a dedicated VPN offered by Amazon, specifically for this purpose. It’s called AWS VPN over Direct Connect. However, you can expect drops in speed and performance, like with a regular VPN – although not as severe.
Should or shouldn’t you use it – that’s entirely up to you?
Which One Should You Use/Choose?

The answer to this question depends on your specific needs. If you need a fast, reliable, and secure connection between your on-premises network and AWS, then Direct Connect is the way to go. Also, if you’re a business owner, DC seems like a reasonable long-term option.
On the other hand, if you need a more affordable option that can be used for personal or small business purposes, then VPN is a good choice. Just keep in mind that VPNs are not as fast or as secure as Direct Connect, so if you are considering using it for business efforts – use it carefully.
Final Thoughts
There you have it – a semi-comprehensive guide to the differences between AWS Direct Connect and VPN. We hope that this article has helped clear some things up for you and that you now feel more confident in choosing the right option for your needs. Thank you for reading!

