Table of Contents
What do syringes, IV bags, and used bandages have in common? Yes, they’re all medical waste that needs to be disposed of! But did you know there are some very specific methods to follow when disposing of this type of waste?
Join us as we explore the most effective methods for medical waste disposal.
Common Disposal Methods
In order to ensure the proper medical waste management disposal, it is important to understand the different disposal methods available. Generally, there are four common disposal methods for medical waste in the United States: incineration, autoclaving, chemical disinfection, and landfill disposal.
- Incineration is one of the most effective ways to destroy hazardous medical waste. This process uses intense heat to reduce medical waste into ash with almost complete destruction of biological contaminants and chemicals.
- Autoclaving uses highly pressurized steam or boiling water to sterilize and render harmless most medical waste as well as any pathogens associated with them.
- Chemical disinfection involves soaking the items in a chemical solution in order to kill microbes and make them safe for disposal. However, care should be taken when using this method as some solutions may be hazardous if not properly handled.
- Landfill disposal is utilized for non-hazardous items such as paper products or packaging materials that are generated during healthcare activities. This ensures that such trash does not end up in public spaces or waterways where it can cause pollution and potentially carry diseases from one place to another.
Benefits of Effective Medical Waste Disposal

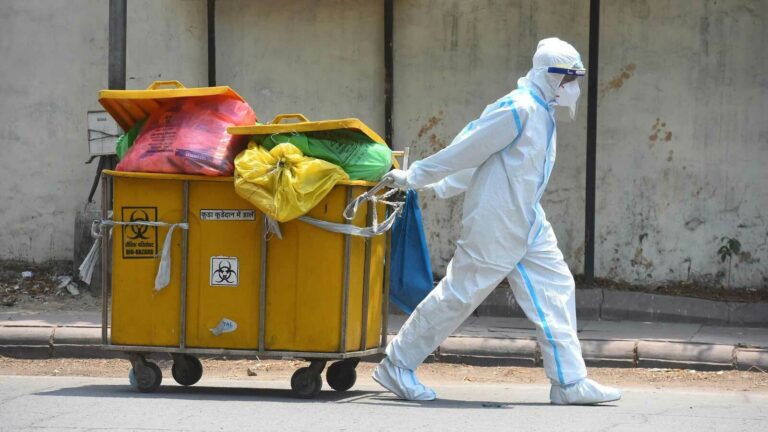
It has become an important issue in recent years. Properly disposing of healthcare waste, including sharps, medical equipment and biohazardous materials, is both a legal requirement and necessary for public health. When they are disposed of correctly, the benefits can be far-reaching.
First and foremost, effective medical waste disposal will help protect public health and increase safety. By disposing of hazardous materials such as needles and syringes in specially-marked containers, we can reduce the risk of accidental needle sticks which can cause bloodborne illnesses such as HIV/AIDS or hepatitis B or C. In addition to increased safety for healthcare workers, proper disposal also ensures that the environment is not contaminated with hazardous substances which could potentially lead to further problems down the line.
Viruses found in human blood and body fluids can survive outside their host for periods of time—if not properly treated or disposed of—and cause epidemics. Additionally, improper disposal can lead to issues with vermin infestations or odors if items are not stored according to guidelines. By complying with regulations on how medical waste should be handled and disposed of properly, hospitals can avoid costly fines while minimizing their environmental impact.

Another benefit is cost savings; by disposing it responsibly through certified vendors that specialize in medical waste management services, facilities save money because they do not have to invest in their own internal infrastructure such as on-site storage space or transportation vehicles. Furthermore they don’t have to worry about the cost associated with viewing documents related to state compliance laws or dealing with any violations due to improper disposal procedures—allowing them to focus more resources on initiatives that more directly contribute towards patient care initiatives instead of administrative tasks related to managing hazardous materials like sharps containers and other regulated items.
Finally it also consolidates responsibility by creating a single source for all their waste management needs—saving time for administrators who no longer need separate vendors for various biohazardous materials ranging from chemicals, tarps, linens, used syringes, swabs, red bag waste, etc. Thus by having an effective strategy in place hospitals will be able to maximize their resources while decreasing organizational expenses long term.
Challenges of Medical Waste Disposal
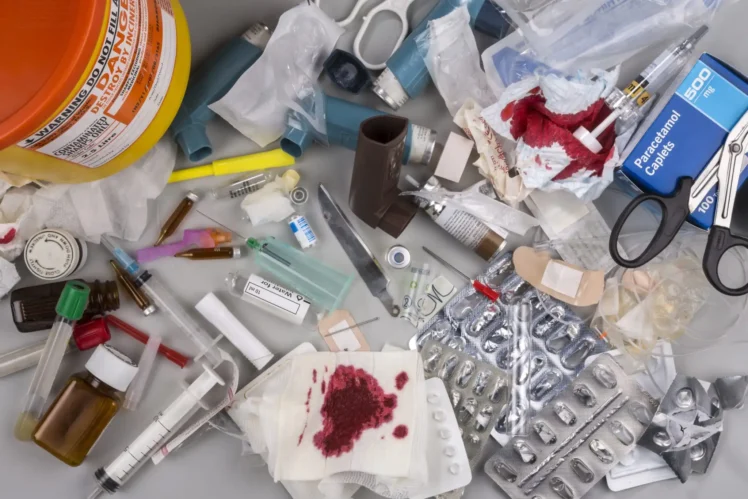
Proper disposal of it is a critical component of public health and safety. Unfortunately, it continues to present significant challenges for health care providers, governments, and the general public. Understanding both the types and the complex rules and regulations that govern its appropriate disposal can help reduce instances of cross-contamination, preserve natural resources, and protect humans from contamination.
Medical waste can be divided into two major categories—regulated medical waste (RMW) and non-regulated medical (NRMW) waste. RMW is considered hazardous under EPA guidelines due to its potential to contain infectious agents or substances that can cause adverse effects on human health. Examples of RMW include any item soiled or contaminated with blood or bodily fluids; sharps (needles, syringes); culture dishes; swabs; specimen containers; and human tissue/organs removed during surgery or autopsy. NRMW includes items such as lab coats, IV tubing, leg casts, x-rays, other nonhazardous solid materials such as bandages or dressings used in patient treatment but are not contaminated with blood or body fluids.
Regulations vary by state but typically require proper segregation of medical wastes via color coding for containers as well as strict adherence to decontamination processes prior to disposal. In some cases these requirements may also call for additional treatments like incineration or autoclaving before disposal into municipal landfills. Ultimately any process used must comply with regional/federal guidelines which may involve additional costs in special handling fees incurred in order to transport the material safely offsite for proper disposal away from local healthcare facilities.
Conclusion
The most effective method for this type of disposal depends on the type of misuse and local regulations. Autoclaving is associated with significant resource costs and requires high set-up costs, but it is a safe way to disinfect certain types of biohazardous waste, preventing potentially hazardous material from entering landfills or waterways. Disposing of medically contaminated items in sharps containers is another cost-effective way to dispose of medical waste safely. Further systems such as mixed or incinerated waste should only be used after considering consequences for the environment and society alike.
Finally, it is essential that all stakeholders – including politicians or governing bodies – become involved in promoting responsible medical waste management through legislative action if necessary in order to ensure the safety and sustainablity of both current and future generations worldwide. Proper management of this health hazard will help reduce risk potentials while protecting people’s health as well as our environment and all living organisms dependent upon it.

